Ethnic Nationalities (252 found)
Burma/Myanmar Election Day: Free-est & Fairest Is Not Free & Fair
On 8 November, Burma/Myanmar held what has been called its “free-est and fairest” election in 25 years. An 80% turnout rate was reported for the 33.5 million Burmese eligible to vote in the election, which saw the first participation of democracy leader Aung San Suu Kyi’s National League for Democracy (NLD) in a general election since the (later annulled) 1990 elections […]
• • •Burma/Myanmar’s 2015 Elections: Obstacles to Inclusive, Credible and Free and Fair Elections
The Union Election Commission (UEC) has received criticism for publishing voter lists that contain numerous errors and for being unable to adequately correct their mistakes. During the initial release of voter lists, complainants noted that the UEC had excluded a number of eligible voters, included voters who were deceased, and printed a number of incorrect information such as birth dates[1]. A subsequent release of voter lists, which the UEC released in order to rectify previous errors, contained further inaccuracies including additional voter exclusions[2]. A particularly drastic example of the incorrect voter lists is the case of Hlaing Tharyar Township, in which 200,000 voters were mysteriously excluded[3]. While there have been numerous cases where citizens have reported incorrect voter lists in remote and rural ethnic areas, such as in Karen State, some villagers do not report to local authorities to have them correct the information due to fear of reprisal […]
• • •မဲဆႏၵရွင္မ်ား၏ေရြးခ်ယ္မႈ ႏွင့္ ၂၀၁၅ ခုႏွစ္ အေထြေထြေရြးေကာက္ပြဲတြင္အမ်ိဳးသမီးမ်ားပါ၀င္မႈ
ၿမန္မာ့ႏူိင္ငံေရးသမုိင္းစဥ္တစ္ေလ်ာက္တြင္ အမ်ိဳးသမီးမ်ားသည္ အၿခားေသာႏူိင္ငံမ်ားနည္းတူ ေရြး ေကာက္ခံကုိယ္စားလွယ္၊ မဲေပးသူ၊ ကုိယ္စားလွယ္ေလာင္း၊ ႏွင့္ တက္ၾကြႏူိးၾကားမႈရွိေသာ ႏူိင္ငံသားမ်ားအၿဖစ္ၿဖင့္ ပါ၀င္ေနခဲ့ၾကသည္။ ၂၀၁၂ ခုႏွစ္ ၾကားၿဖတ္ေရြးေကာက္ပြဲအၿပီးရရွိေသာ ကိန္းဂဏန္း မ်ားအရ ၿပည္ေထာင္စုလႊတ္ေတာ္ႏွင့္  ၿပည္နယ္ ႏွင့္တုိင္းေဒသၾကီးလႊတ္ေတာ္ ႏွစ္ရပ္ စလုံး၌ အမ်ိဳးသမီးလႊတ္ေတာ္ကုိယ္စားလွယ္ ၅၃ ဦး (၄.၆%) ပါ၀င္ၿပီး ၿပည္သူ႔လႊတ္ေတာ္တြင္ ၂၅ ဦး (၇.၈%)၊ အမ်ိဳးသားလႊတ္ေတာ္တြင္ ၄ ဦး (၂.၄%)၊ ၿပည္နယ္ႏွင့္ တုိင္းေဒသၾကီး လႊတ္ေတာ္ တြင္ ၂၄ ဦး (၃.၆%) ရွိသည္ၿဖစ္ရာ က်ားမတန္းတူညီမွ်ေရးအတြက္ အနိမ့္ဆုံးလုိအပ္ခ်က္ၿဖစ္ သည့္ အၿပည္ၿပည္ဆုိင္ရာ စံႏႈန္း ၃၀% ၿပည့္မွီရန္ မ်ားစြာလုိပါေသးသည္ […]
ၿပည္နယ္ ႏွင့္တုိင္းေဒသၾကီးလႊတ္ေတာ္ ႏွစ္ရပ္ စလုံး၌ အမ်ိဳးသမီးလႊတ္ေတာ္ကုိယ္စားလွယ္ ၅၃ ဦး (၄.၆%) ပါ၀င္ၿပီး ၿပည္သူ႔လႊတ္ေတာ္တြင္ ၂၅ ဦး (၇.၈%)၊ အမ်ိဳးသားလႊတ္ေတာ္တြင္ ၄ ဦး (၂.၄%)၊ ၿပည္နယ္ႏွင့္ တုိင္းေဒသၾကီး လႊတ္ေတာ္ တြင္ ၂၄ ဦး (၃.၆%) ရွိသည္ၿဖစ္ရာ က်ားမတန္းတူညီမွ်ေရးအတြက္ အနိမ့္ဆုံးလုိအပ္ခ်က္ၿဖစ္ သည့္ အၿပည္ၿပည္ဆုိင္ရာ စံႏႈန္း ၃၀% ၿပည့္မွီရန္ မ်ားစြာလုိပါေသးသည္ […]
Fear & Voting in Burma/Myanmar: 2015 Election
On 8 November, up to 32 million Burmese voters will elect representatives to fill 1,171 seats in the National and State/ Division Parliaments. Ninety one political parties will compete for 75% of seats in the legislature, while 25% remain reserved for the Tatmadaw. Despite official promises of a “free and fair” election, multiple flaws continue to undermine the credibility of the process […]
• • •UN General Assembly 2015: Updates since the 2014 UNGA Resolution on Burma/Myanmar
The Burmese authorities have failed to implement most of the recommendations from previous United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) resolutions, despite recent ones being adopted by consensus, in particular Resolution 69/248 adopted in 2014. The information presented in this briefer refers directly to the language proposed for the 2015 UNGA Resolution. In 2015, authorities continued to either fail to address, or collude in serious human rights violations, and took steps to undermine the possibility of ‘free and fair’ elections on 8 November […]
• • •A New Briefing by Burmese Rohingya Organisation UK: No Hope For Rohingya From Burma Election
When the people of Burma go to the polling stations on November 8th, for the first time since independence the majority of Rohingya will not be allowed to vote. In another first, as all Rohingya candidates for the national parliament were rejected by the Union Election Commission (UEC), there will be no Rohingya MPs in Parliament […]
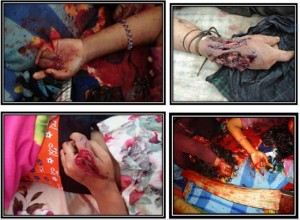
• • •Naypyidaw’s escalated offensive in central Shan State displaces over 6,000; four civilians injured by indiscriminate shelling and shooting
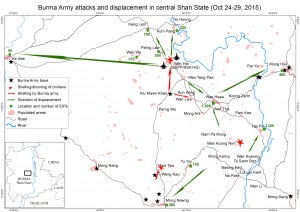 The SHRF strongly condemns the escalated attacks in the past week by the Burma Army against the Shan State Progress Party/Shan State Army (SSPP/SSA) in central Shan State, involving indiscriminate shelling and shooting of civilians. The attacks have caused displacement of over 6,000 civilians from 22 villages in three townships since early October […]
The SHRF strongly condemns the escalated attacks in the past week by the Burma Army against the Shan State Progress Party/Shan State Army (SSPP/SSA) in central Shan State, involving indiscriminate shelling and shooting of civilians. The attacks have caused displacement of over 6,000 civilians from 22 villages in three townships since early October […]
Half Empty: Burma’s Political Parties and their Human Rights Commitments
 On 8 November 2015, Burma’s electorate will vote for the representatives who will sit in Parliament from 201b to 2021. The polls are anticipated to usher in a Parliament that will be markedly different from the body that was installed as a result of the November 2010 election and the April 2012 by–elections […]
On 8 November 2015, Burma’s electorate will vote for the representatives who will sit in Parliament from 201b to 2021. The polls are anticipated to usher in a Parliament that will be markedly different from the body that was installed as a result of the November 2010 election and the April 2012 by–elections […]
Presidential Hopefuls in Myanmar’s 2015 Elections
Myanmar’s General Elections being held on 8 November 2015 will determine the Assembly of the Union (Pyidaungsu Hluttaw) which comprises of the Lower House of Parliament (People Assembly, Pyithu Hluttaw) and the Upper House of Parliament (National Assembly, Amyotha Hluttaw) as well as the regional assemblies of the fourteen states and regions […]
• • •Justice Delayed, Justice Denied: တရားမႈရွာဘုိ႔ ေႏွာင့္ေႏွးျခင္းမွာ၊ တရားမႈကိုျငင္းပယ္ျခင္းပါ။
 ျမန္မာႏုိင္ငံတြင္ ၂၀၁၀ ခုႏွစ္ေနာက္ပုိငး္မွစတင္၍ ျဖစ္ေပၚလွ်က္ရွိေသာ ဒီမုိကေရစီအသြင္ကူး ေျပာင္းမႈဟူသည့္ေအာက္ ၌ႏုိင္ငံေရးအာဏာ၏ အခန္းက႑အားပို၍ အေလးထားလာၾကသည္းအေဘာရွိသည္ […]
ျမန္မာႏုိင္ငံတြင္ ၂၀၁၀ ခုႏွစ္ေနာက္ပုိငး္မွစတင္၍ ျဖစ္ေပၚလွ်က္ရွိေသာ ဒီမုိကေရစီအသြင္ကူး ေျပာင္းမႈဟူသည့္ေအာက္ ၌ႏုိင္ငံေရးအာဏာ၏ အခန္းက႑အားပို၍ အေလးထားလာၾကသည္းအေဘာရွိသည္ […]

 All posts
All posts